The FTP is an old but effective file transfer protocol between computers on local networks or the Internet, being widely used by web hosting systems. However, it is considered unsafe by today’s standards and modern browsers are abandoning support. Learn more about what FTP is.
What is FTP?
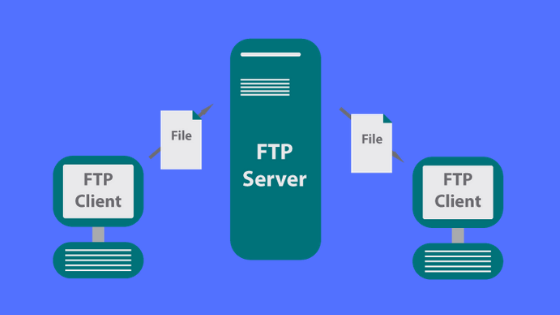
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is a protocol used to transfer files over a computer network, from one l
ocation to the internet. Basically, it allows the direct exchange of files between two computers, where one gains access to the folders of the other.
The protocol is the oldest means of transferring data between computers on a network, having originated in 1971 and uses the client/server model, where the former accesses data and the latter stores it.
Cloud data storage is another client/server model just like FTP, except that data is not stored on a single computer.
How FTP Works
FTP uses a server as the computer responsible for hosting the files. The client is the user who will make the access. The connection is always authenticated with username and password, while the server is usually accessed by an IP address.
Any computer can be used as an FTP server, although nowadays it is mostly used by website administrators, who use the connection and a hosting system to maintain their page data. There are several third party programs for managing FTP connections, such as free File
Zilla, one of the most popular.
Is the protocol secure?
As we have explained, FTP is almost 50 years old and therefore does not have a number of security standards supported by modern web browsers, although it is pos
sible to supplement the SSL protocol (FTPS) to provide more secure connections.
Both Google and Mozilla are currently looking at ways to completely remove protocol support from Chrome and Firefox respectively, which will lead users still using the protocol to administer websites or access files relying on third-party clients, rather than doing so. browser access.
